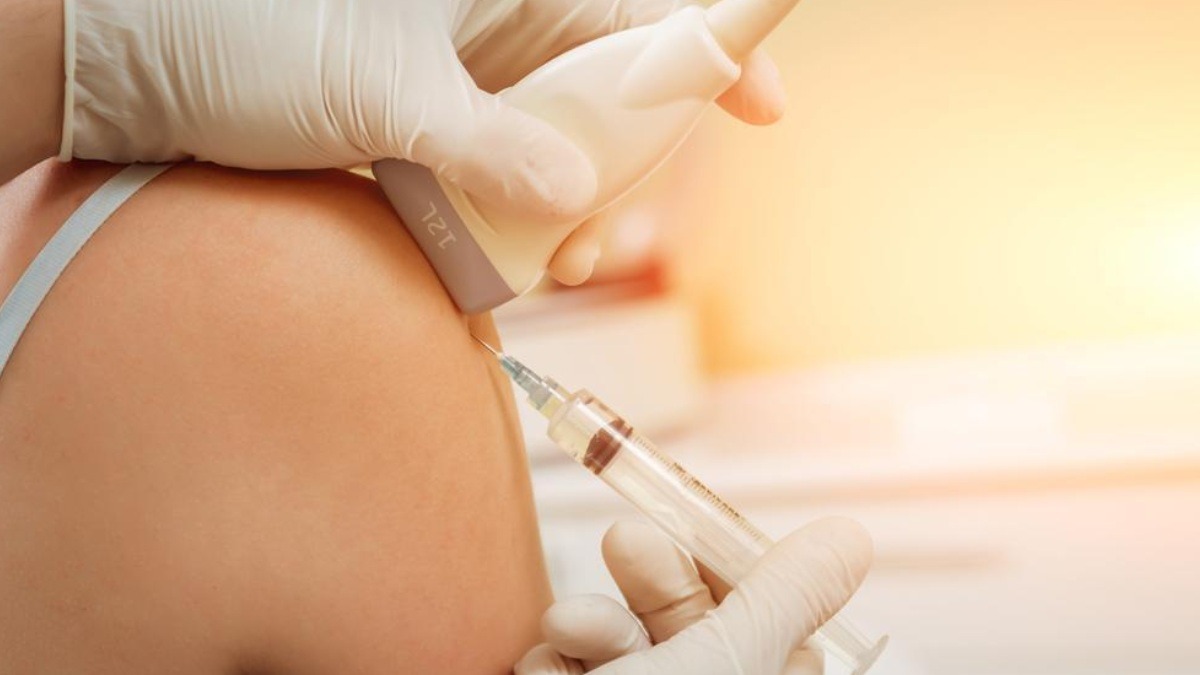
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) therapy is a cutting-edge regenerative treatment that leverages the body’s own healing capabilities to treat a variety of musculoskeletal conditions. By concentrating platelets from a patient’s own blood and injecting them into injured or painful areas, PRP therapy can promote tissue repair, reduce inflammation, and provide significant pain relief.

What is Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy?
PRP therapy involves the extraction of a small amount of a patient’s blood, which is then processed to concentrate the platelets. Platelets are a type of blood cell that plays a crucial role in healing by releasing growth factors and other proteins that aid in tissue repair and regeneration.
- Blood Collection:
- A small sample of the patient’s blood is drawn, typically from the arm.
- Centrifugation:
- The blood sample is placed in a centrifuge, a machine that spins the blood at high speeds to separate its components. This process concentrates the platelets, producing a plasma with a high platelet count.
- PRP Preparation:
- The platelet-rich plasma is collected from the centrifuge and prepared for injection.
- Injection:
- The PRP is injected into the injured or painful area. Ultrasound or fluoroscopic guidance is often used to ensure precise placement of the injection.

Mechanism of Action
Platelets contain a variety of growth factors and cytokines that are essential for healing. When injected into damaged tissues, PRP releases these bioactive proteins, which:
- Stimulate Cellular Repair:
- Growth factors like platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β), and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) promote the proliferation and differentiation of cells involved in tissue repair.
- Enhance Collagen Production:
- Collagen is a vital component of connective tissues such as tendons, ligaments, and cartilage. PRP boosts collagen synthesis, improving the structural integrity of these tissues.
- Reduce Inflammation:
- PRP modulates inflammatory responses, reducing pain and swelling in the affected area.
- Promote Angiogenesis:
- The formation of new blood vessels, or angiogenesis, is stimulated by PRP, enhancing blood flow to the injured area and supporting tissue regeneration.

Benefits of PRP Therapy
PRP therapy offers several advantages over traditional treatments for pain management:
- Natural Healing:
- Utilizes the body’s own healing mechanisms, reducing the need for synthetic drugs or invasive procedures.
- Minimally Invasive:
- PRP injections are performed on an outpatient basis and require minimal recovery time.
- Reduced Risk of Adverse Reactions:
- Because PRP is derived from the patient’s own blood, the risk of allergic reactions or infections is significantly minimized.
- Long-Lasting Pain Relief:
- PRP not only addresses pain but also promotes long-term healing, providing sustained relief and functional improvement.

Conditions Treated with PRP Therapy
PRP therapy is versatile and can be used to treat a variety of musculoskeletal conditions, including:
- Tendinitis and Tendinosis:
- Conditions such as tennis elbow (lateral epicondylitis), golfer’s elbow (medial epicondylitis), and Achilles tendinitis can benefit from PRP, as it enhances tendon healing and reduces pain.
- Osteoarthritis:
- PRP can be injected into osteoarthritic joints (e.g., knees, hips, shoulders) to reduce pain, improve joint function, and potentially slow the progression of cartilage degeneration.
- Muscle Strains and Ligament Sprains:
- Acute and chronic injuries to muscles and ligaments, such as hamstring strains and ankle sprains, can heal more rapidly with PRP therapy.
- Rotator Cuff Injuries:
- PRP can aid in the healing of partial rotator cuff tears and reduce pain in the shoulder.
- Plantar Fasciitis:
- Chronic heel pain caused by plantar fasciitis can be alleviated with PRP injections, promoting healing of the plantar fascia.
- Chronic Back Pain:
- PRP can be used to treat degenerative disc disease and facet joint arthritis, providing relief from chronic back pain.

Procedure and Expectations
- Consultation:
- The process begins with a consultation where the healthcare provider reviews the patient’s medical history, performs a physical examination, and may order imaging studies to confirm the diagnosis and determine the appropriateness of PRP therapy.
- Preparation:
- On the day of the procedure, the patient’s blood is drawn and processed to create PRP.
- Injection:
- The PRP is injected into the target area using ultrasound or fluoroscopic guidance. The entire procedure typically takes less than an hour.
- Post-Procedure:
- Patients may experience mild soreness or swelling at the injection site, which usually subsides within a few days. They are often advised to rest and avoid strenuous activities for a short period.
- Follow-Up:
- Follow-up appointments are scheduled to monitor the patient’s progress and determine if additional PRP injections are needed. Most patients begin to notice improvements within a few weeks, with continued progress over several months.

Conclusion
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) therapy represents a promising frontier in pain management, offering a natural, minimally invasive option for treating a variety of musculoskeletal conditions. By harnessing the body’s own healing capabilities, PRP can provide effective pain relief, promote tissue regeneration, and improve overall function.
At ALGOS, we are dedicated to utilizing advanced regenerative treatments like PRP to help our patients achieve optimal health and well-being. If you’re experiencing chronic pain or a musculoskeletal injury, consult with us to determine if PRP therapy is the right solution for you.